中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (49): 8015-8019.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.49.025
• 器官移植动物模型 organ transplantation and animal model • 上一篇 下一篇
复发性口腔溃疡家兔模型补充超氧化物岐化酶的作用
胡 静1,朱建华1,王 帅2
- 1佳木斯大学附属口腔医院,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154002;2佳木斯大学附属第一医院,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154002
Rabbit models of recurrent aphthous ulcer replenished with superoxide dismutase
Hu Jing1, Zhu Jian-hua1, Wang Shuai2
- 1Stomatological Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2First Hospital Affiliated to Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
背景:复发性阿弗他溃疡的具体发病机制目前医学界尚无定论,其中体内氧自由基的增多是引起复发性口腔溃疡反复发作的原因之一。
目的:观察超氧化物歧化酶对复发性阿弗他溃疡治疗效果的影响。
方法:在24只复发性阿弗他溃疡家兔模型建立后,按随机数字表法分为3组。模型对照组作为对比不做处理;阴性对照组家兔每天局部碘甘油擦拭;超氧化物歧化酶组家兔每天进行超氧化物歧化酶生物胶囊溶液灌胃,溃疡局部用碘甘油进行擦拭。1周后切取口腔溃疡病变组织进行对比研究。各组家兔造模后,每隔3 d上午同一时间兔耳静脉采血,流式细胞仪分析T细胞亚群CD3+、CD4+、CD8+以及CD3+/CD8+变化。
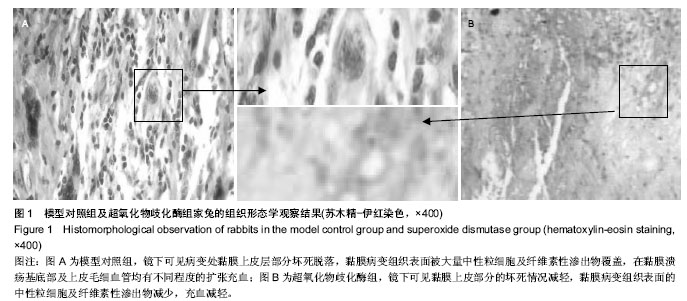
结果与结论:当溃疡病变形成后,模型对照组和阴性对照组家兔外周血中细胞CD3+、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+的比值经过统计均明显低于正常,而CD8+细胞数远远大于正常数值。超氧化物歧化酶组灌服超氧化物歧化酶生物胶囊后,CD3+、CD4+细胞数开始逐渐升高,而CD8+细胞数则相反呈下降趋势。提示应用氧自由基的天然清除剂超氧化物歧化酶就能有效清除溃疡面中过量的氧自由基,从而达到临床上治疗复发性阿弗他溃疡的目的。
中图分类号:

.jpg)